Jupyter Notebook on Local Machines
Overview
The Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Uses include: data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning, and much more.
At Dartmouth, Jupyter is commonly used to interactively develop Python and R programs, but it is a versatile and extensible environment that is capable of running a broad array of languages, including C/C++, Java, Go, Matlab, and many more.
You can read more about the project at https://www.jupyter.org.
Installing conda
The most straightforward way to install and start using a Jupyter environment is through the Anaconda distribution, which is an open-source Python distribution that includes the conda package manager that makes installing, maintaining, and upgrading Python and R environments straightforward.
Detailed installation instructions found at Anaconda.com are linked below:
Managing Packages with conda
We are only listing a few of the more useful commands here. You can add --help to the end of any conda command to get some help on how to use it.
Complete documentation for conda can be found at
https://conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/.
conda create- make a new environmentconda env remove- remove an existing environmentconda info -envs- show environmentsconda install <package name>- add a package to an environmentconda remove <package name>- remove a package from an environmentconda list- show packages installed in an environmentconda search <package name>- show available packagesconda activate <environment name>- activate (use) an environmentconda deactivate- deactivate an environment
Installing conda packages into an existing environment
Using the conda install command, you can request multiple packages on the command line and specify (or not) a version for each one. Here is an example of installing a specific version of the numpy package and whatever is current for the ldap3 package into the myenv environment.
Note: part of what conda does dependencies so you would also be installing a couple dozen packages required by numpy and jupyter, if you run this command:
conda install numpy=1.16.2 jupyterHow do I know if a package is available?
Use the conda search command for this or search for the package on
Anaconda.org. You will find that a vast majority of the Python packages are supported by Anaconda or one of the community maintained channels.
Installing Jupyter
Since Jupyter is merely a Python package, you can use conda to simply install Jupyter as follows:
conda install jupyterThis will install the latest Anaconda supported versions of Jupyter and Python along with all the necessary dependencies.
Launching Jupyter
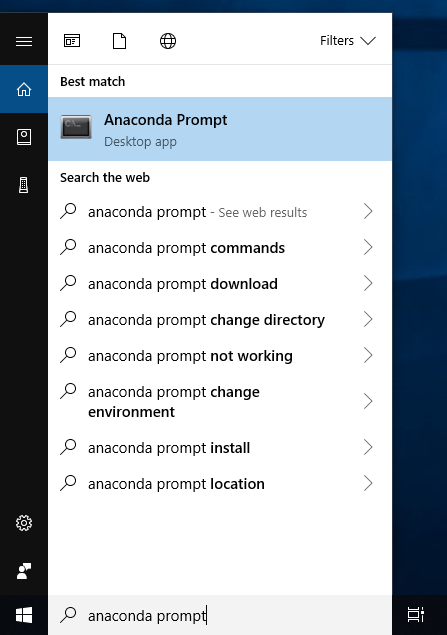
- Windows. From the Start menu, search for and open “Anaconda Prompt”:
-
macOS. Open Launchpad, then click the terminal icon.
-
Linux. Open a terminal window.
Running Jupyter Notebook Server
Now that you have a terminal or Anaconda Prompt window open, to launch a Jupyter notebook server type jupyter notebook.
This will automatically open a new web browser window or tab and show the Notebook Dashboard.